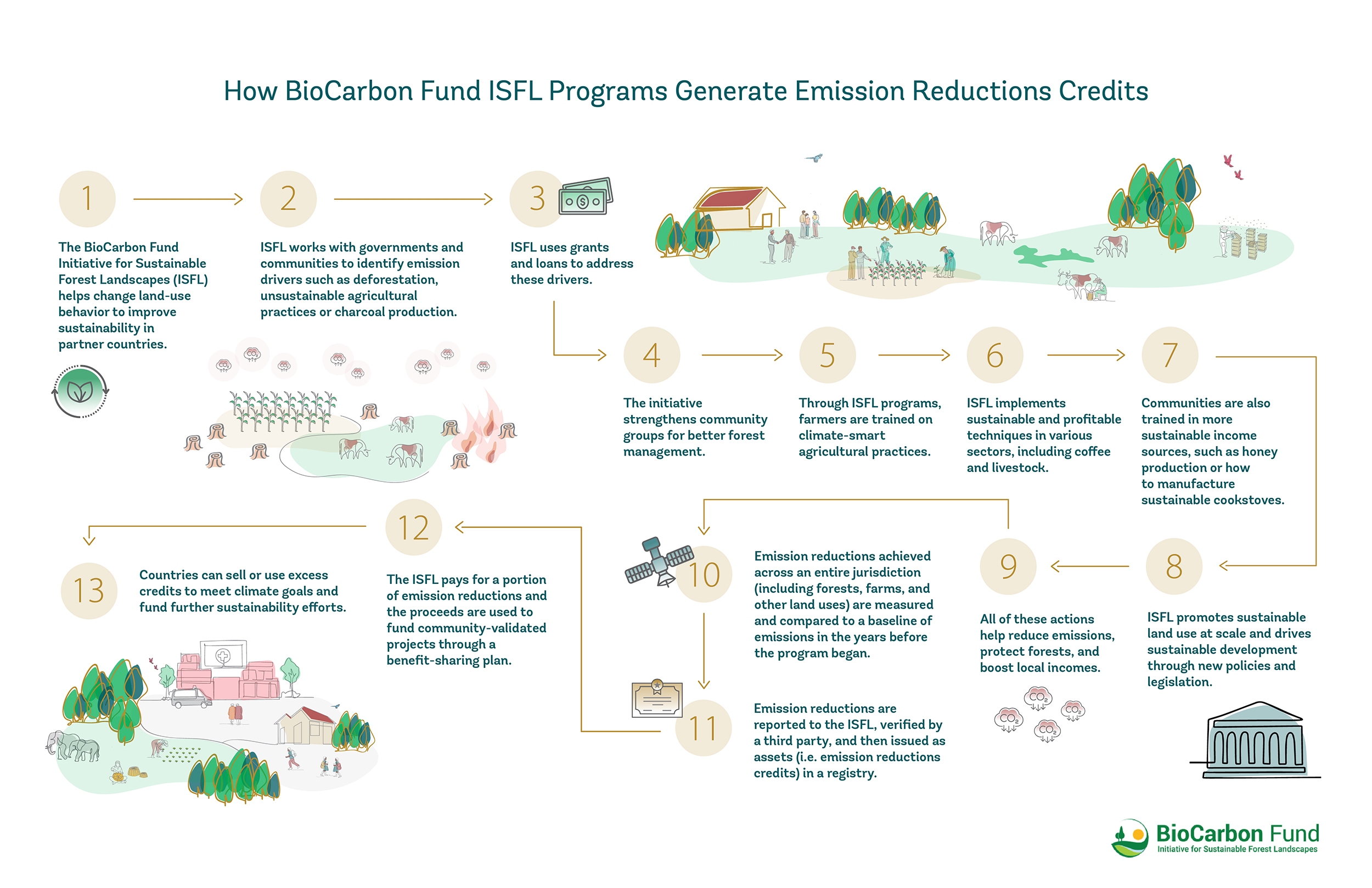
Results Based Climate Finance is an evolving approach to sustainable development that aims to incentivize climate action, create and expand carbon markets, and stimulate innovation. ISFL’s innovative use of results-based climate finance and focus on integrated landscape management were positively highlighted by the recent Mid-Term Evaluation conducted in FY24. Through this approach, investors or others (including donors) pay an entity to achieve, report on, and independently verify a set of pre-agreed performance targets related to climate mitigation. Basically, reducing greenhouse gas emissions in a sustainable manner.
The Emission Reduction programs use selected methodologies for carbon accounting, to measure the reductions generated by their programs, which become the results that lead to climate finance flowing.
The value of these programs depends on the robustness of the methodology used, and the stronger the methodology the more robust the results. Of course, all programs, which implement the activities that generate the results need to be tailored to the local context, and be designed to maximize social impact and social inclusion.
Results Based Climate Finance programs improve accountability and funding effectiveness, because payments are only disbursed after results have been verified. As such, investors can be more certain that their contributions are creating a real impact on the earth.
However while Results-Based Climate Finance serves a very important role in incentivizing change, ISFL is also learning that changing land use behaviour from all actors – from farmers to enterprises to governments, can also be effected by other drivers. Farmers are more than willing to adopt climate smart practices when they see that these practices will raise their yields and generate higher incomes, even before they are offered a results based incentive.